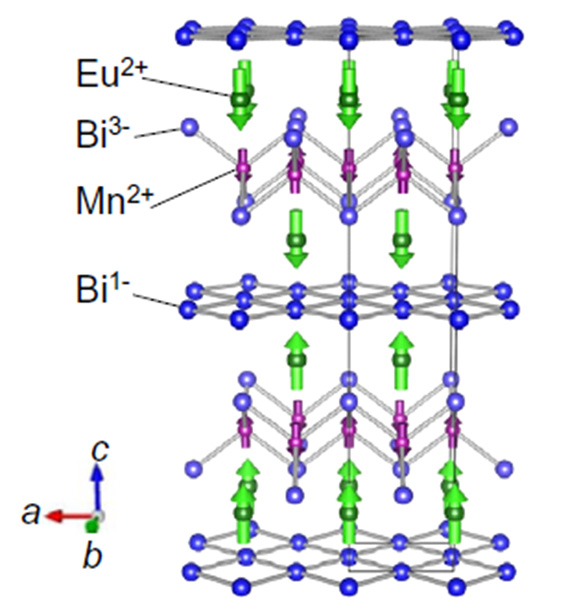
For the innovation of spintronic technologies, Dirac materials, in which low-energy excitation is described as relativistic Dirac fermions, are one of the most promising systems because of the fascinating magnetotransport associated with extremely high mobility. To incorporate Dirac fermions into spintronic applications, their quantum transport phenomena are desired to be manipulated to a large extent by magnetic order in a solid.
We report a bulk half-integer quantum Hall effect in a layered antiferromagnet EuMnBi2, in which field-controllable Eu magnetic order significantly suppresses the interlayer coupling between the Bi layers with Dirac fermions. In addition to the high mobility of more than 10,000 cm2/V s, Landau level splittings presumably due to the lifting of spin and valley degeneracy are noticeable even in a bulk magnet. These results will pave a route to the engineering of magnetically functionalized Dirac materials.
This research was conducted through collaborative research with Tokyo University, Osaka University, RIKEN, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization and IMR. This article carried in Science Advances.
detail1: press release (in Japanese) [PDF:940KB]
detail2: Science Advances Website [DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1501117]