Industrial and automotive machinery, such as automotive engine parts, contain materials that are, heat-, wear-, and corrosion-resistant. They are known as “super engineering plastics,” and they continue to revolutionize manufacturing processes. While they are actually plastic, they are much stronger than the typical plastics we encounter in everyday life. These materials, however, create a corrosive environment during manufacturing.
That’s changing with a new innovation developed by a team of researchers based in Japan. They designed a new method to improve the wear and corrosion resistance of the machines that produce super engineering plastics. The researchers published their results on August 27 in npj Materials Degradation, a Nature journal.
“The global market for super engineering plastics has grown in recent years because they have remarkably high-temperature resistance, good mechanical strength and exceptional chemical and solvent resistance in high-temperature environments,” said Kenta Yamanaka, paper author and associate professor of deformation processing at the Institute for Materials Research at Tohoku University. “However, during the manufacturing process, the reciprocating screw in the manufacturing apparatus usually suffers from frequent wear loss because the semi-fluid raw materials commonly contain a large number of glass fibers as reinforcement.”
Super engineering plastics also decompose into sulfuric gas, inducing a highly corrosive environment in addition to the high physical wear conditions. The screws in the manufacturing machines cannot withstand such an environment for long.
To correct this issue, Yamanaka and the researchers studied a steel alloy known as high-speed steel, which is currently mainly used for tools. According to Yamanaka, the steel has outstanding mechanical properties at room and elevated temperatures, but it’s vulnerable to corrosion.
The researchers used an alloy based on high-speed steel and treated it with copper.
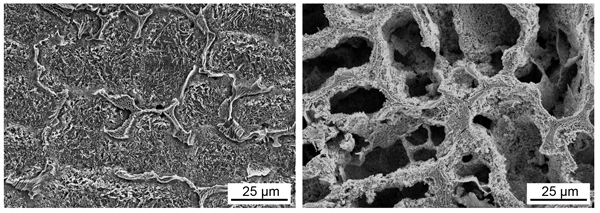
Surface appearance of the developed steel containing copper (left)
and copper-free counterpart (right)
Image credit: Kenta Yamanaka et al, Tohoku University
“The wear and corrosion resistance of steels generally show a trade-off relationship,” Yamanaka said. “In this study, we demonstrate that adding trace copper to high-hardness steels significantly improves the corrosion resistance of the alloys, resulting in an excellent combination of wear and corrosion resistance.”
After analyzing the alloy through imaging and experimental studies, the researchers found that they had successfully developed a highly wear and corrosion-resistant steel. Next, they plan to further investigate the alloy’s properties for application in other fields.

Screw for plastic injection molding, as fabricated with the developed steel.
Image credit: Kenta Yamanaka et al, Tohoku University
This work was supported by the Adaptable and Seamless Technology Transfer Program through Target-Driven Research & Development from the Japan Science and Technology Agency and the ISIJ Research Promotion Grant from the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan.
Publication Details
Authors
Chen Zhang, Kenta Yamanaka, Huakang Bian, Akihiko Chiba
Journal
DOI
Published online
August 27, 2019
Press release online (in Japanese)
PDF: 827KB
